First Law of Thermodynamics
First Law of Thermodynamics: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as first law of thermodynamics, forms of first law of thermodynamics and first law of thermodynamics for various processes.
Important Questions on First Law of Thermodynamics
of water at is converted into steam at by boiling at atmospheric pressure. The volume of water changes from as a liquid to as steam. The change in internal energy of the system during the process will be (Given latent heat of vaporisation , Atmospheric pressure
Given below are two statements:
Statement I: If heat is added to a system, its temperature must increase.
Statement II: If positive work is done by a system in a thermodynamic process, its volume must increase.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below
A source supplies heat to a system at the rate of If the system performs work at a rate of The rate at which internal energy of the system increases is
The amount of heat supplied to a gas in a system is equal to , the system in return does of work on the surrounding. Find change in internal energy of the gas.
If amount of heat given to the system be Joules and the amount of work done by the system is . If initial internal energy of the system is . Final internal energy of the system is
In the case of diatomic gas, the heat given at constant pressure is that part of energy which is used for the expansion of gas, is
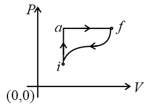
What is for the process described by figure. Heat supplied during the process is .
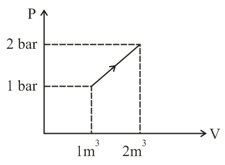
ideal gas expands from volume to,. This may be achieved by either of the three processes: isobaric, isothermal and adiabatic. Let be the change in internal energy of the gas, be the quantity of heat added to the system and W be the work done by the gas. Identify which of the following statements is false for?
of water at atmospheric pressure has volume of and when boiled it becomes of steam. The heat of vaporization of water is . Then the change in its internal energy in this process is
How the first law of thermodynamics can be justified? Give an example in support of your answer.
An ideal gas is expanded adiabatically at an initial temperature of so that its volume is doubled. The final temperature of the hydrogen gas is
In an insulated container of water is stirred with a rod to increase the temperature. Which of the following is true?
of water is heated from to , if its volume remains constant, then the change in internal energy is (specific heat of water )
A diatomic gas does of work when it is expanded isobarically. The heat given to the gas in the process is
Two moles of a monoatomic gas undergoes an isobaric process. If the gas temperature is increased by then the heat absorbed by the gas is (Take )
of liquid water at undergoes a phase change into steam at at atm (take it to be ). The initial volume of the liquid water was which is changed to of steam. Find the change in the internal energy of the system.
[Use heat of vaporization ]
In the indicator diagram, we have
(a) Change in internal energy along ABC is .
(b) Work done along path AB .
(c) .
(d) Heat absorbed by the system along path AD is .
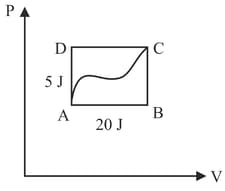
Calculate:
(i) Change in internal energy along the path CDA.
(ii) Heat given to the system along path ABC.
(iii) Value of
(iv) Change in internal energy along AD.
State first law of thermodynamics.
Consider the following cycle (a-b-c) for ideal gas in the figure: b-c(adiabatic), c-a(isobaric), and a-b (isochoric). Calculate work done by the gas and heat absorbed by the gas for each path, a-b, b-c, c-a. What is the total work done and heat absorbed for the full cycle?
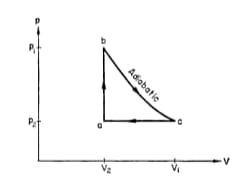
In the diagram shown and cal. If cal for the curved path value of for path , will be